Leather Insights: A Comprehensive Guide for Buying the Best Leather
Types of Leather
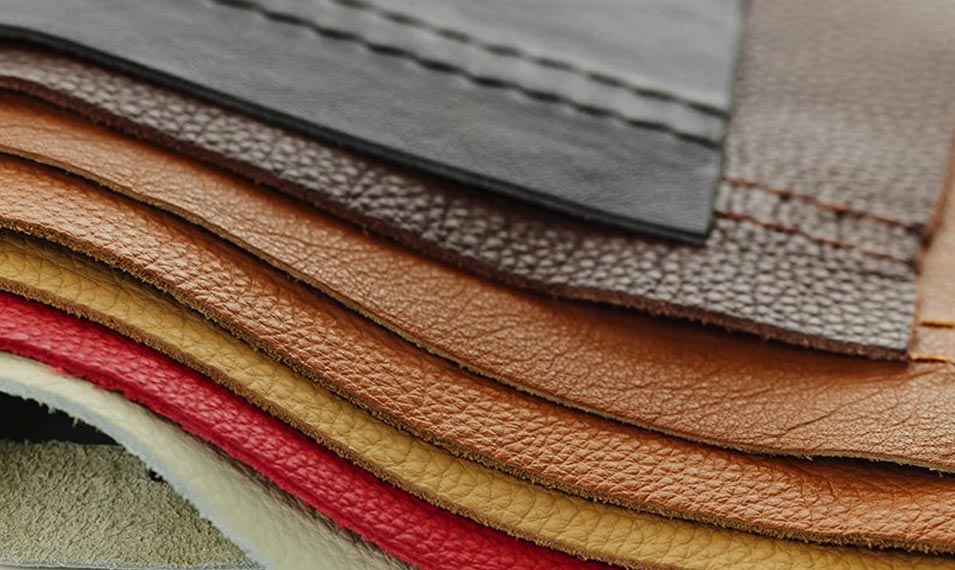
The quality of leather varies greatly. You have most likely seen different labels on leather items, such as top grain or genuine. These are simply different types of leathers based on their quality.
They are nothing but different types of leathers based on their quality.
Now, can you get the best bang for your buck? Yes, you can.
Knowing where to buy leather is just not enough, you must learn to distinguish between different types of leather. You will need to understand why some materials last longer than others and why a particular leather bag costs thousands, while others cost a fraction of that price.
So, what is the best leather? The best quality leather will depend on these important factors, most notably:
- Type of animal and breed
- Physical location and climate where the animal lived
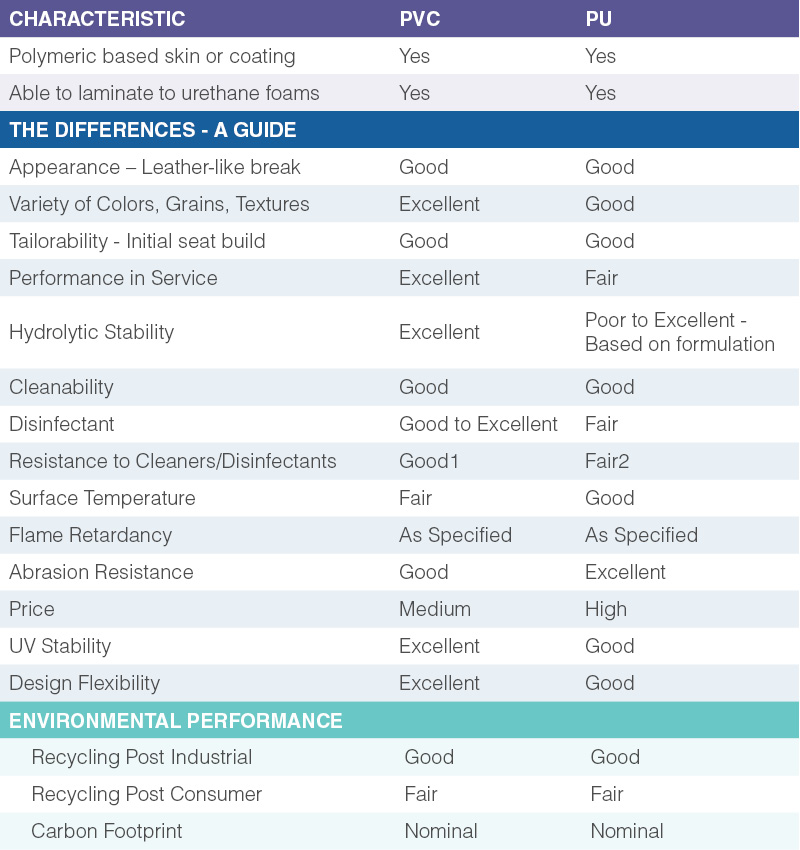
- The portion of the hide the leather was cut from (see diagram below)
- The layer of the hide that is used (top grain, full grain, split)
- Quality and skill of the processing and tanning

Different breeds of cows will produce different quality hides due to their genetics and environment. Hot climates tend to have insects that bite the animal and leave scars whereas cold climates don’t suffer from pests as much. Certain breeds might have more protective hair or thicker skins due to the weather.
Different portions of the hide also yield different quality leather. For instance, the lower portion, as shown in the diagram above, tends to have looser fibers that make up the hide. The looser fibers sponge and swell when wet. Lower portions of the hide also tend to get marked much easier from insects and scrapes like barbed wire fencing. There are also more wrinkles in the hide around the legs, neck and head. These scars and wrinkles become permanent and are almost impossible to remove in the processing of the leather.
Different layers within the hide also have an enormous impact on quality. Full grain leather and top-grain are the best. See our in depth focus on the grain vs split just a few paragraphs further down to know which portion you are buying.
Finally, knowing exactly how to take a raw hide and process it through tanning and finishing is a sought after skill and will influence the quality of the final product significantly. Italian leather is admired for this very reason – as Italian leather artisans are considered amongst the most skilled in the world.
In general, there are four types of leather. These include Full Grain Leather, Top Grain Leather, Corrected Grain Leather, and Bonded Leather. Take a look at the picture below. See how the fibers run both horizontally and vertically in different parts of the hide.
Buying leather with more horizontal fibers wears out quickly because they can readily pull apart. Vertically running fibers, however, are the strongest. In other words, the higher the number of vertical fibers, the better.
A. Full Grain Leather
Full grain leather comes from the top layer of the hide. It includes all the grain with it – hence the name full grain leather. This type of leather retains the inherent toughness, as well as the imperfections because there are no surface alterations or splitting.
It is the highest quality leather and the only one suitable for saddleback. Thus, it is also the most expensive. Working with this leather material is challenging. It absorbs body oils and develops a patina over time – a characteristic that attributes to its popularity.
Common Uses: Saddlebacks, sought-after leather products.
B. Top Grain Leather
Top grain is the second highest grade of leather. Usually, to obtain top grain leather, the top layer of skin from blemished hides is split. The surface is sanded to get rid of inherent imperfections. Pigmentation or staining gives the leather an attractive look.
This also makes top grain leather smoother and more flexible than the full grain. Although this type of leather is strong and durable, it tends to stretch permanently over time. It is used to produce suede and nubuck. Most high-end products, such as handbags and jackets, are comprised of top grain leather.
Common Uses: Suede and nubuck-making, making high-end products such as handbags and jackets.
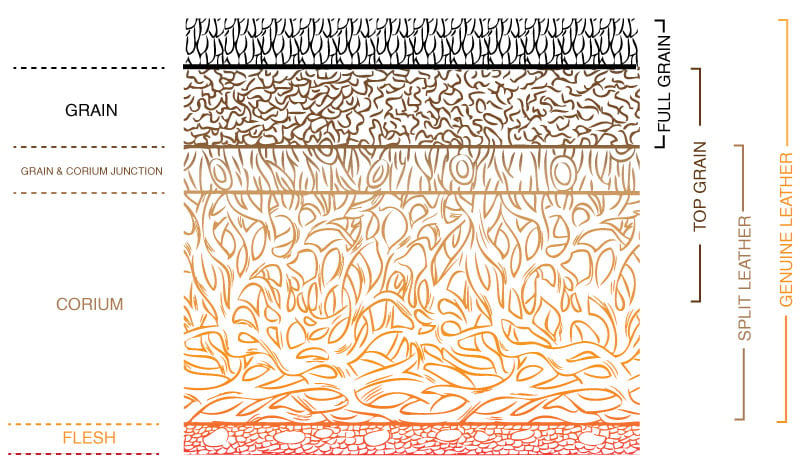
C. Corrected Grain (Bottom Cut/Split) Leather
Corrected grain or split leather, also known as genuine leather, is produced using the skin layers that remain after the top is split off and from the corium predominantly (see diagram above). Split leather tends to be tougher in texture due to the fact that is resides under the top layers and is mostly used in applications that don’t require the leather to be soft like furniture backs and sides. Just like the top grain leather, it is also sanded to remove natural imperfections. Usually, the surface is spray painted and embossed with a leather-like pattern to resemble natural appearance. However, the processing alters the inherent breathability of the leather.
Common Uses: Making jackets, handbags, messenger bags, accessories, footwear, and furniture.
D. Bonded Leather
Bonded leather is made up of leftovers of the hide. This includes the dust and shavings. These are bonded together using polyurethane or latex on top of a fiber sheet. It is often spray-painted to look like full or top grain leather. You can’t determine the percentage of natural leather unless the manufacturer chooses to disclose it – which is very unlikely. Bonded leather is the lowest (and the cheapest) grade of leather.
Common Uses: Making furniture, bookbinding, and various fashion accessories.
Though there are four basic types of leather, you can find a wide range of options based on the percentage of organic material, durability, and the finishing process.
Aniline Leather: It is the most natural leather with minimal resistance to soiling. Generally, soft and tanned animal hides, such as Napa, are subject to dying in a drum with aniline dyes exclusively. Aniline dyes are translucent and water-soluble dyes that bring out the natural markings, scars, and wrinkles in the hide.
It develops a natural patina over time. As this process is suited to only high-quality animal hides, it is one of the most expensive leathers in the world. It also needs regular upkeep.
Common Uses: Making luxury accessories such as wallets, bags, jackets, and sought-after furniture.
Semi-Aniline Leather: Semi-aniline leather consists of a light surface coating with a small amount of pigment. Thus, it is stronger than aniline leather but maintains its natural look. It also exhibits stain resistance to some extent.
Corrected Grain Pigmented Leather: While preparing corrected grain pigmented leather, manufacturers subject the hides to sanding and buffing to remove imperfections such as scars and bite marks. Manufacturers often emboss the treated surface with artificial grain and sprayed with a sealer top-coat. This coating lends a more plastic feel to the leather.
The look of corrected grain leather may vary considerably, depending on the embossing and pigmentation process. There are different grades of corrected grain leather. Normally, less corrected grain means better leather quality. It is perhaps the most widely-used leather around the world.
Common Uses: Making jackets, handbags, messenger bags, accessories, footwear, and furniture.
Pigmented Leather: A polymer surface coating, containing certain pigments, is applied to produce the desired look and properties. Due to its durability, pigmented leather is often used to make furniture and car upholstery.

Embossed Leather: Embossed leather is leather with artificial patterns imprinted on the natural grain of animal skin using heat and high pressure. Typically, steel plates with different engraved designs are used to create embossed leather for a variety of applications, including upholstery and accessories.
The most common types of embossing include blind embossing, gold embossing, and color imprint. While blind embossing involves imprinting patterns without any color, gold embossing includes using gold films for imprinting. Color imprint, on the other hand, uses color films for the embossment. Sometimes, the leather may also be bonded with foam and lining to allow the embossed patterns to retain their shape for longer.
Common Uses: Leather furniture, accessories such as bags and jackets, and upholstery.
Finished Split Leather: Split leather is a single layer of leather separated from the animal hide. Usually, the middle or lower section of the hide is used to produce split leather. When it is coated with a polymer and embossed to resemble natural leather-like look, it becomes finished split leather. You can also treat this type of leather with various embossing patterns and finishing touches. Finishing is required to get a surface resembling the finished full-grain leather.
However, it is almost always used in low-stress applications as finished split leather is considerably weaker than grain leather. It is also virtually impossible for the naked eye to differentiate between full grain pigmented leather and finished split leather.
Common Uses: Leather accessories and furniture.
Nappa Leather: “Nappa” is a generic name for soft, dyed leather usually used in advertising. There is no distinct test to characterize nappa leather.
Nubuck Leather: Aniline dyed leather is typically used to produce nubuck leather, which comes from the top grain of the hide. It is sanded on the grain side to create a velvety appearance. This velvety appearance and feel often attract shoppers into buying nubuck leather products.
The buffing or sanding removes the visible markings and defects in the top grain. Staining or dying further removes the defects left after buffing. Being made from top-grain leather, nubuck is more durable compared to suede or bonded leather. However, it is susceptible to environmental factors such as mud, dirt, and grit. That’s why nubuck shoes are suited for trekking and other outdoor activities.
Common Uses: Shoes, jackets, wallets, handbags, travel bags, briefcases, and furniture, among other leather items.
Oil Tanned Leather: Producing oil-tanned leather involves processing it with natural oils after the initial vegetable tanning is complete. Most tanneries use fish oil, particularly cod oil, for the tanning process. The purpose is to create a remarkably smooth and flexible finish. These qualities enhance its workability making oil-tanned leather more suitable for textured leather products.
The oil treatment also lends higher water and moisture resistance. It can also fend of scuff marks or minor scratches quickly, a feature all outdoor leather products must have. But most importantly, oil-tanned leather is revered for its beauty. It is available in a variety of stunning colors and finishes. It also develops a gorgeous patina over time.
Common Uses: Outdoor leather gear such as shoes, jackets, bags, and coats, among others.
Pigmented Leather: To create pigmented leather, a polymer surface coating containing pigments is applied to create the desired look and properties. It is rarely good-quality as a layer of colored polyurethane and varnish often alters the qualities of the hide.
Pigmented leather has uniform surface and color without any inherent defects of the animal skin. It is extremely durable and requires less maintenance. It also offers high resistance against scratches and stains.
Sometimes, however, over-coating can lend it plastic-like an appearance. The pigmentation also reduces its breathability. Due to its durability and low maintenance, pigmented leather is often regarded as the best leather for furniture, especially in the affordable price range.
Common Uses: Furniture, accessories, and car upholstery.
Semi-Aniline Leather: Generally, high-quality hides are used to create semi-aniline leather with a thin layer of protection (polyurethane) to retain the natural aesthetics. The base surface coating has a small amount of pigment while other coats have only dye. Thus, semi-aniline leather is stronger compared to the aniline leather, but maintains its natural look. It also exhibits stain resistance to some extent.
Common Uses: Primarily to make upholstery and furniture.
Suede: Suede is one of the most popular leather types with a napped finish. Made from the underside of the animal hide such as lamb, goat, calf, pig, and deer, it comes with an attractive finish. As it is thinner and less durable, suede is also vulnerable to damage. It is one of the best grades of leather revered for its look and feel, not durability.
Common Uses: It is used to make jackets, shoes, shirts, purses, curtains, gloves, and furniture.
Common Uses: Insides, interiors, and linings.

Pigmented Leather Texture

Pigmented Leather Seat
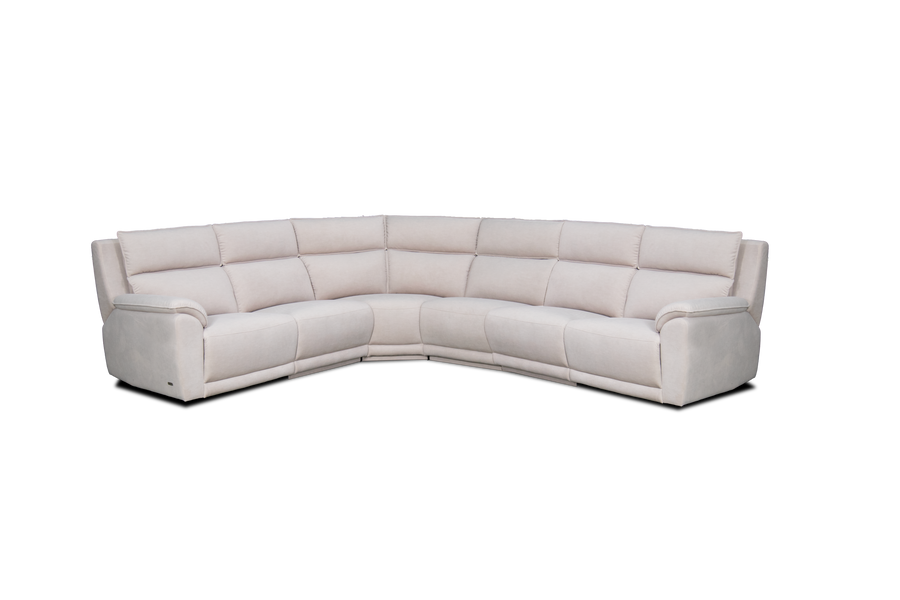
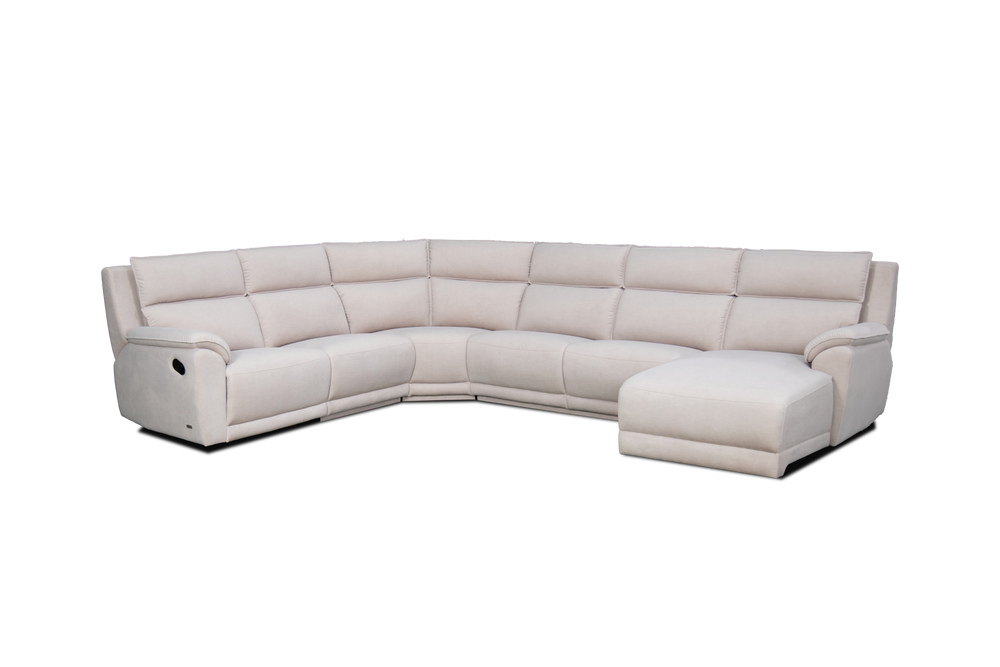
Leather for Furnitures
One of the most popular leather item categories is furniture. High-quality leather furniture can last for years. However, each type comes with unique characteristics. In other words, you need to choose the right type of leather to get the most out of your furniture. Hopefully, this quick leather furniture buying guide will help you.

Leather Alternatives
Polyurethane (PU) vs Polyvinylchloride (PVC) Furniture
When it comes to buying leather furniture, people often use the terms polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) leather interchangeably. However, they are distinctly different. You must understand this difference if you want to get the best bang for your buck while purchasing leather furniture.
1) Polyurethane (PU) Leather
- Polyurethane leather is composed of polyurethane, bicast, or ground leather. Thus, it closely resembles natural leather.
- It provides a soft and flexible seating surface.
- It offers better breathability (vapor transmission), compared to PVC leather.
- The high-performance PU leather can quickly adjust to body temperature. It can remain cool even after sitting for long periods of time.
- However, it is susceptible to direct sunlight and humidity. Prolonged exposure can make it brittle.
- It comes with high abrasion resistance, durability, and inherent stain resistance.
- It is not naturally flame resistant. But, resistants are often added during the manufacturing process.
- Though it is more economical than natural leather, polyurethane upholstery tends to be expensive compared to PVC leather furniture.
2) Polyvinylchloride (PVC) Leather
- Though polyvinylchloride (PVC) resembles the softness, color, and texture of natural leather, it doesn’t contain natural leather at all.
- It is very durable and inherently flame resistant.
- It has a relatively better resistance to cleaners and disinfectants, compared to PU leather.
- Affordability and an excellent variety of color, texture, and grain are the primary reasons why this leather is the most popular one out there.
PU and PVC leathers are also known as faux leather and as they are not made from animal products, they can also be called vegan leather.